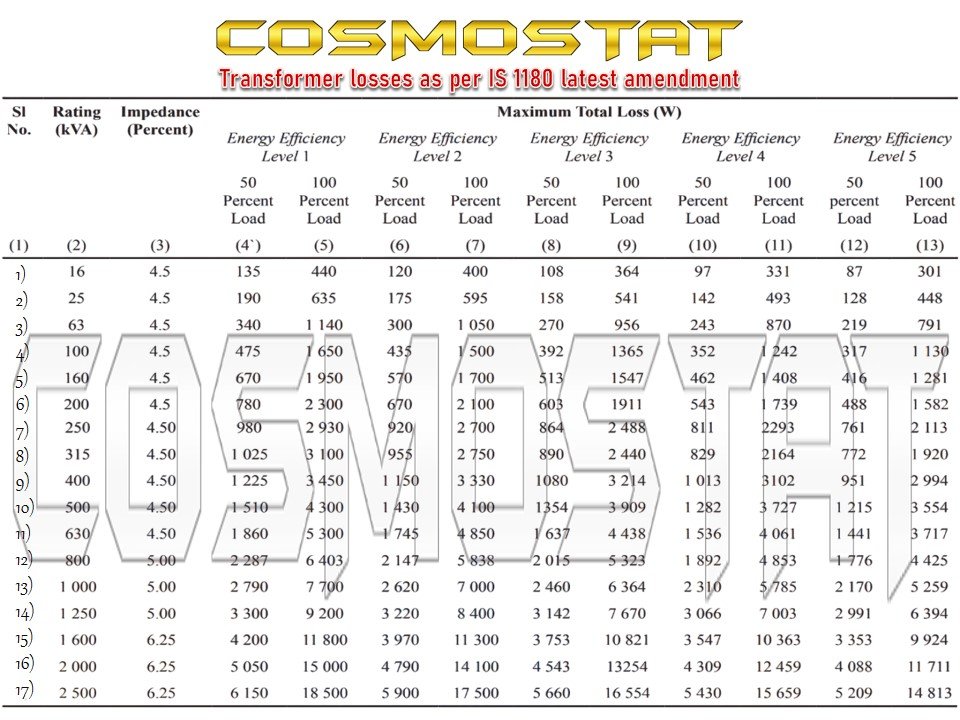
Distribution Transformer Losses as per IS 1180
Distribution transformers are critical components of the electricity grid that help step down the voltage of electricity from transmission levels to levels suitable for consumption by end-users. However, distribution transformers can also be a significant source of energy losses, contributing to higher energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. In India, where the demand for electricity is growing rapidly, it is crucial to adopt energy-efficient distribution transformers to ensure sustainable and efficient use of energy resources.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has set a standard for energy-efficient distribution transformers known as IS 1180. The standard specifies the maximum losses that a transformer can have at rated voltage and frequency, as well as the minimum efficiency that the transformer should achieve. By adhering to the IS 1180 standard, manufacturers can ensure that their transformers meet the required energy efficiency levels, leading to significant energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The losses in a distribution transformer can be divided into two categories: no-load losses and load losses. No-load losses are the power consumed by the transformer when it is energized but not supplying any load. Load losses are the power consumed by the transformer when it is supplying load. The sum of the no-load losses and the load losses gives the total losses of the transformer.
The IS 1180 standard sets maximum limits for the no-load losses and the load losses based on the rating of the transformer. For instance, for a 100 kVA transformer, the maximum no-load losses are 0.3 kW, and the maximum load losses are 1.8 kW. The minimum efficiency that the transformer should achieve is also specified based on the rating of the transformer.
The standard divides transformers into two categories: level 1 and level 2. Level 1 transformers have higher losses compared to level 2 transformers. The no-load losses and the load losses of level 1 transformers are 30% and 20% higher, respectively, than the losses of level 2 transformers.
The IS 1180 standard also specifies the test methods and procedures for measuring the losses of the transformer. The tests should be conducted in accordance with the Indian Standard IS 2026, which specifies the requirements for power transformers.
The losses in a distribution transformer depend on various factors, such as the design of the transformer, the quality of the materials used, the operating conditions, and the load cycle. By optimizing these factors, manufacturers can reduce the losses in the transformer, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Adopting energy-efficient distribution transformers as per the IS 1180 standard can help utilities and industries to save on energy costs and reduce their carbon footprint. It can also help India achieve its energy efficiency and sustainability goals while ensuring a reliable and stable power supply to consumers.
In conclusion, distribution transformers are critical components of the electricity grid that have a significant impact on energy efficiency and sustainability. The IS 1180 standard provides a framework for manufacturers to design and produce energy-efficient distribution transformers that can reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint. By adopting these standards, India can achieve its energy efficiency and sustainability goals while ensuring a reliable and stable power supply for its citizens.
